What We Do
We are unraveling the functional complexity of the human 3D biology using
Light-Field Microscopy integrating Artificial Intelligence for real-time 3D imaging and analysis.
Real-time 3D Imaging Platform
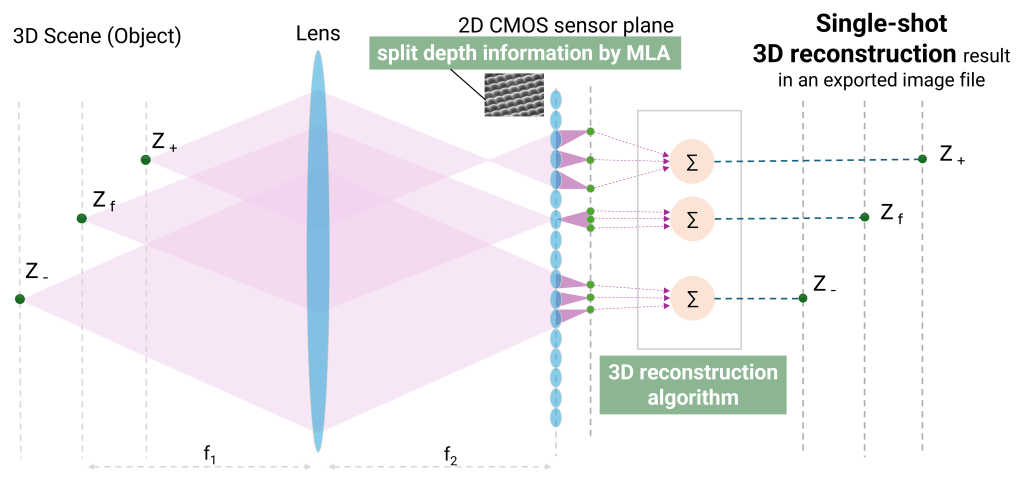
Light-field microscopy is an advanced imaging technique that captures 3D information from a single snapshot by recording both the intensity and direction of light rays. A microlens array is used to split light rays with depth information, enabling 3D image reconstruction with specialized algorithm and software.
GPU-accelerated Computational 3D Reconstruction
- Parallel computations over 10,000 depth estimations from a single-shot.
- Real-time 3D reconstruction in 100 ms.
- Experience the unprecedented speed of microscopic 3D imaging.

Application —
3D Cell Biology
It can capture all the live functional signals of fluorescently labeled molecules of interest in organotypic 3D cell cultures in a single-shot.This enables real-time 4D spatio-temporal analysis, allowing for more comprehensive and precise quantitative analysis of drug responses in mini-organs.
Application —
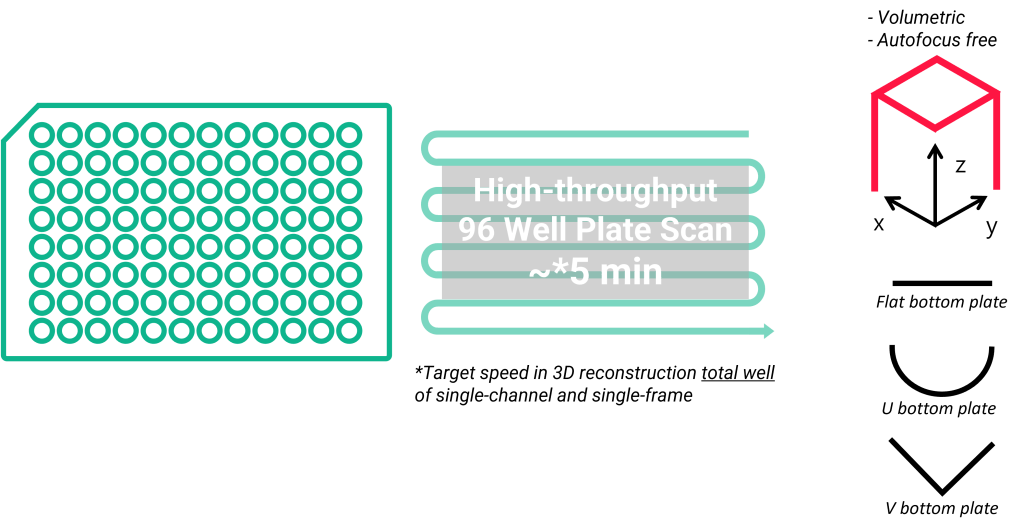
High-throughput in 3D
A Power of Real-time 3D Imaging – It can obtain real-time assay data for 3D mini-organs through 3D imaging without z-stacking. This allows for multi-well plate-based 3D high-throughput assays at previously impossible time intervals.
- Scanning flat, U-bottom and V-bottom 96 wells in 3D per 9 minutes (current record)
- A 3D data in 2D storage size
- Multi-channel fluorescence for high-content analysis
Product Line Up
CHEETAH™
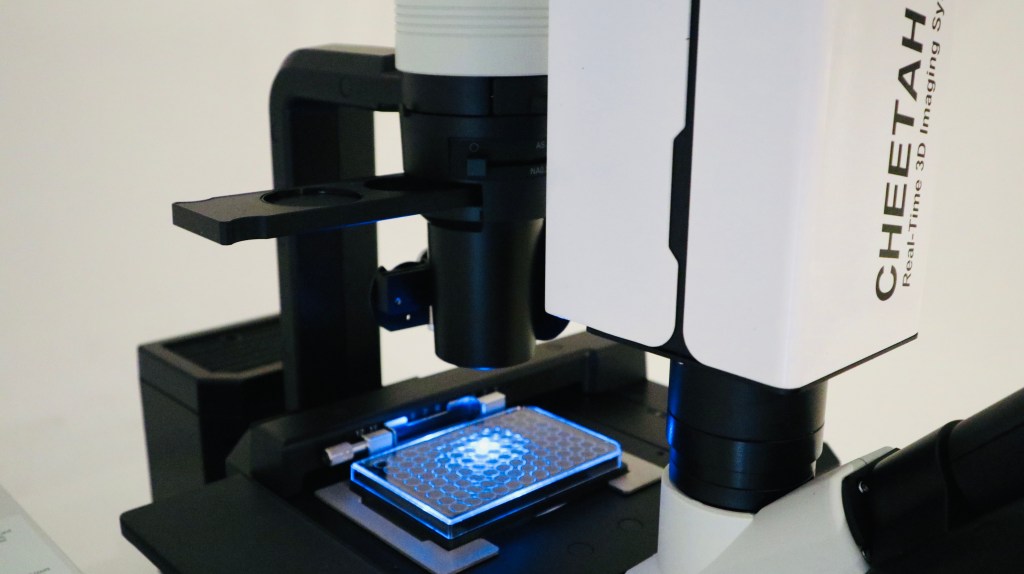

Scientific Instrument – Analyze mechanism-of-action (MOA) in depth of organotypic 3D cell culture with unprecedented volumetric frame rate (>30fps).
QField™

Human-relevant 3D Cell-based Assay Platform – A new approach enables quantitative measurement of biological activity in 3D cell cultures, offering high precision in assessing the potency, safety, and mechanism-of-action (MOA)-specific effectiveness and inhibition of potential therapies in higher throughput manner. This method leverages predictive, human data-driven models to enhance preclinical efficacy and safety validation, providing a more accurate and reliable assessment of drug candidates.